iSCSI, which is short for Internet Small Computer System Interface, is a SCSI (Small Computer System Interface) transport protocol for mapping of block-oriented storage data over TCP/IP networks. It enables universal access to storage devices and storage area networks (SANs) over standard TCP/IP networks. This post will introduce iSCSI SAN and how it works in details.
Since iSCSI SAN is often compared with Fibre Channel and FCoE, this part will focus on Fibre Channel vs iSCSI vs FCoE SANs.
iSCSI and Fibre Channel are both designed for storage area networks,which are respectively called iSCSI SANs and FC SANs. And for its strong performance and reliability, Fibre Channel has long been considered as the common technology for company SAN applications. However, FC SANs are costly and complex to manage and implement. Thus iSCSI SAN has become an increasingly popular alternative to Fibre Channel SAN because it provides solid performance for companies working with smaller budgets. Furthermore, iSCSI SAN uses traditional Ethernet network components (such as Ethernet switches, servers and so on) for connectivity between hosts and storage devices, which make it much cheaper to be implemented. Then you may ask: iSCSI vs Fibre Channel SANs, which one to choose? It all depends on your needs. FC SANs tend to be faster with lower latencies/higher IOPS (Input/output operations per second). While iSCSI SANs are simpler and less expensive.
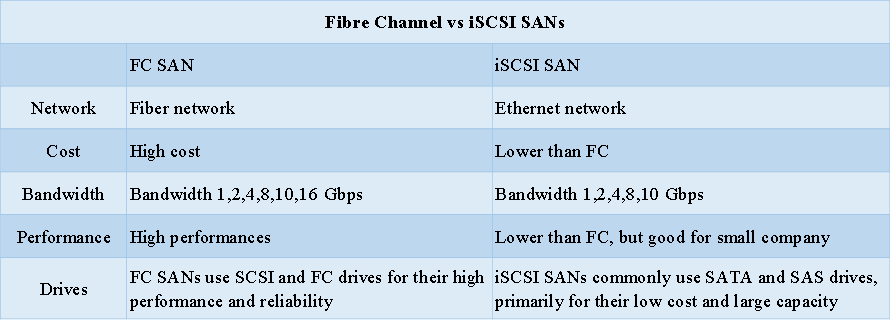
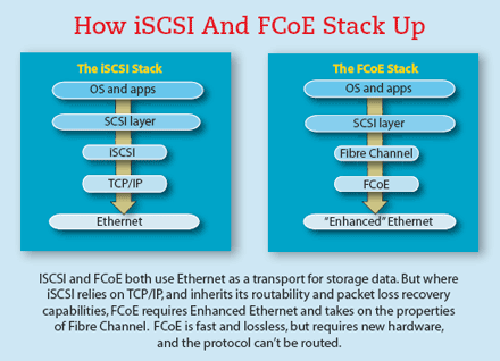
Both iSCSI and FCoE are IP-based storage networking standards. But each has their own features. FCoE is short for Fibre Channel over Ethernet, which is a new industry standard. It allows Fibre Channel frames to be encapsulated over Ethernet networks. While iSCSI is a more mature technology to provide block-level access to storage devices by carrying SCSI commands over standard TCP/IP Ethernet. Furthermore, iSCSI SAN is relatively simple to setup and troubleshoot, and it can run on any IP network. FCoE SAN requires Data Center Bridging and Converged Network Adapters all running at 10 Gbps or faster. For higher cost, It is now usually used in applications where there are Fibre Channel hardware, software, and expertise.
Usually, iSCSI SAN uses an ordinary IP network to transport block-level data between an iSCSI initiator on a server and an iSCSI target on a storage device. The followings are how it works:
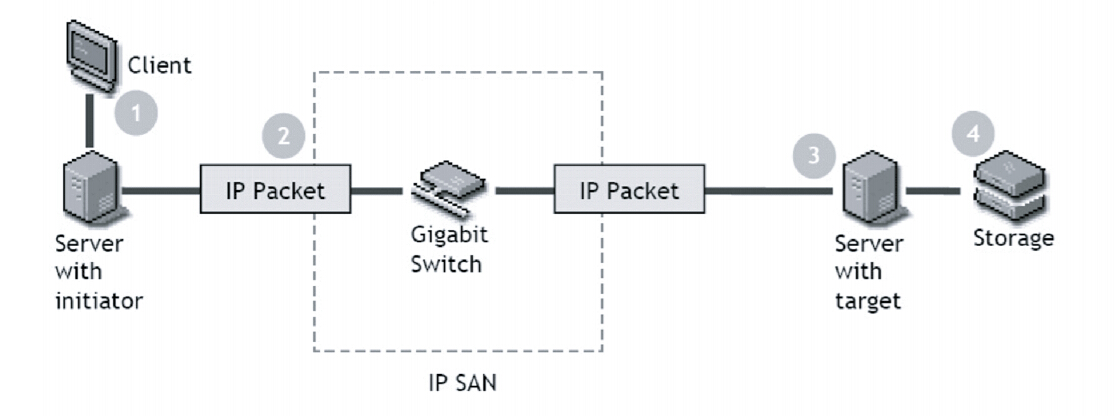
1.An application or user wants to access data or file from the server;
2.Server with initiator converts the SCSI commands into the iSCSI command, which then sent to the IP SAN using a point-to-point connection;
3.After getting the packet the receiving side disassembles and processes the packet;
4.The target converts these IP packets into SCSI commands and issues to the storage. Security is provided through iSCSI authentication and virtual private networks (VPNs), as needed.
Note: The initiator is the one who requests for the data to be read from or written to the storage. And the target is responsible for processing commands from the initiator.
To sum up, iSCSI offers a number of advantages for companies such as flexibility, lower cost and simplified management. And an iSCSI SAN is a perfect choice for users who are interested in moving to networked storage.