In the data centers, tremendous amount of business data needs to be transmitted, processed and stored. Fiber optic links are vital for providing the bandwidth and speed needed to transmit huge amounts of data to and from a large number of sources. Transmission speeds at core switches are increasing and backbone infrastructures are experiencing a significant upsurge in the amount of fiber optic cabling. The 24-fiber trunking and interconnect solution, allowing enterprise data center managers to effectively migrate from 10G to 40/100G, offers the right 10-40-100G migration path. Why say so? Keep reading and you will find the answer.
The IEEE ratified the 802.3ae standard for 10G over fiber using duplex-fiber links (one for transmitting and the other for receiving) in 2002. In 2010, the IEEE ratified the 802.3ba standard for 40G and 100G by using parallel optics, or multiple lanes of fiber transmitting at the same speed. Running 40G requires 8 fibers, with 4 fibers each transmitting at 10G and 4 fibers each receiving at 10G, while running 100G requires a total of 20 fibers, with 10 transmitting at 10G and 10 receiving at 10G. Both scenarios call for high-density multi-fiber MPO connectors.
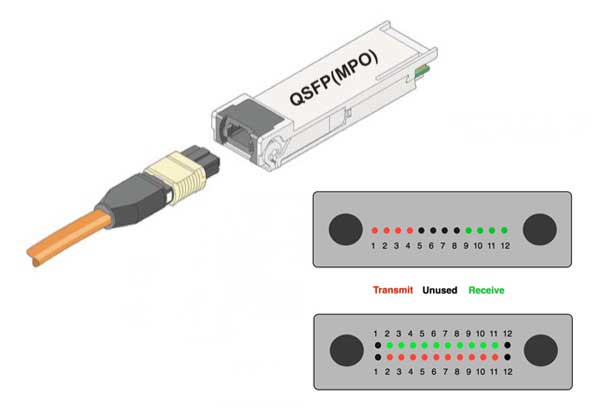
For 40G, a 12-fiber MPO connector is used. Because only 8 optical fibers are required, typical 40G applications use only the 4 left and 4 right optical fibers of the 12-fiber MPO connector, while the inner 4 optical fibers are left unused. To run 100G, a 24-fiber MPO connector is recommended, with the 20 fibers in the middle of the connector transmitting and receiving at 10G and the 2 top and bottom fibers on the left and right unused.
According to the IEEE 802.3ba standard, multimode optical fiber supports both 40G and 100G over link lengths up to 150 meters while using OM4 optical fiber and up to 100 meters when using OM3 optical fiber. It is important to note that single-mode fiber can also be used for running 40G and 100G to much greater distances using wavelength division multiplexing (WDM). While this is ideal for longer-reach applications, for most data center applications of less than 150 meters, single-mode fiber are not feasible due to expensive costs. Copper twinax cable is also capable of supporting 40G and 100G but only to distances of 7 meters.
The use of 24-fiber trunk cables can support 10G, 40G and 100G applications. For 10G applications, each of the 24 fibers can be used to transmit 10G, for a total of 12 links. For 40G applications, which requires 8 fibers (4 transmitting and 4 receiving), a 24-fiber trunk cable provides a total of three 40G links. For 100G, which requires 20 fibers (10 transmitting and 10 receiving), a 24-fiber trunk cable provides a single 100G link. Some benefits of using 24-fiber trunk cables are listed below.
- Maximum Fiber Use
As mentioned previously, 40G uses 8 fibers of a 12-fiber MPO, leaving 4 fibers unused. When using a 12-fiber trunk cable, those same 4 fibers are unused. For example, three 40G links using three separate 12-fiber trunk cables would result in a total of 12 unused fibers, or 4 fibers unused for each trunk. With the use of 24-fiber trunk cables, data center managers actually get to use all the fiber and leverage their complete investment. Running three, 40G links over a single 24-fiber trunk cable uses all 24 fibers of the trunk cable. This recoups 33% of the fibers that would be lost with 12-fiber trunk cables, providing a much better return on investment.
- Reduced Cable Congestion
Less cable congestion in already-crowded pathways is another benefit of 24-fiber trunk cable. Space is premium in the data center, and congested cable pathways can make cable management more difficult and impede proper airflow needed to maintain efficient cooling and subsequent energy efficiency. The 24-fiber trunk cables are appreciably larger than 12-fiber trunk cables. For a 40G application, it takes three 12-fiber trunk cables to provide the same number of links as a single 24-fiber trunk cable, which may need 1.5 times more pathway space.
- Easier Migration Path
The 24-fiber data center fiber trunking and interconnect solution offers a simple and cost-effective migration path from 10G to 40G and 100G. With 24-fiber trunk cables effectively supporting all three applications, upgrading the cabling infrastructure is as simple as upgrading the hydra cables or cassettes and patch cords to the equipment.
The 24-fiber data center trunking and interconnect solution helps data center managers effectively and efficiently support today’s high-speed requirements. With 24-fiber trunk cables that eliminate the need for complete and complex reconfiguration all the way from the switch to the equipment, it offers an easy, cost-effective method for upgrading from 10G, to 40G and 100G with the least capital and operating expense.
Related Article: http://www.fiberopticshare.com/12-fiber-or-24-fiber-mtpmpo-cabling-which-is-better-for-40g100g-network.html
