In recent years, telecommunications has undergone significant changes. Fiber optics are steadily replacing copper wire as an appropriate means of signal transmission. A variety of optical equipment is attributable to this communication evolution, during which fiber optic cables are leading the way. An optical fiber is a flexible and transparent fiber made by drawing glass (silica) or plastic to a diameter slightly thicker than that of a human hair. Plastic optical fiber vs. glass optical fiber: which is more preferable?
Plastic optical fiber, polymer optical fiber or POF, is an optical fiber which is made out of plastic. Traditionally, it comprises of PMMA (acrylic) as the core (96% of the cross section in a fiber 1mm in diameter) that facilitates the transmission of light, and fluorinated polymers as the cladding material. Plastic fiber uses harmless green or red light that is easily visible to the eye. Plastic fibers can be safely installed in a home without risk to inquisitive children. But nowadays, a higher-performance plastic fiber is used based on perfluorinated polymers. The following picture shows the construction of the plastic optical fiber.
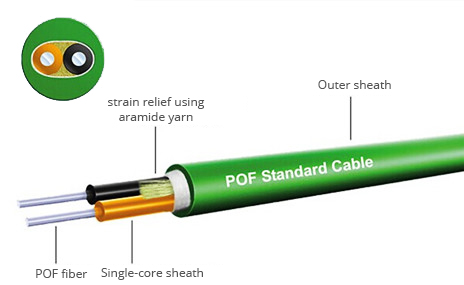
Glass optical fiber, just as its name shows, is an optical fiber made of glass. Being a delicate type of optical fiber, it cannot be cut, spliced or repaired, less resistant to flexibility and accidental breakage. Glass fiber optic cables are extremely versatile and robust and available in a mix of configurations, end fittings and adapter types. However, this kind of optical fiber is generally ideal for hostile environments. Even when exposed to mechanical stress, high temperatures or chemical substances, it performs normal operation. A figure about the construction of glass optical fiber is available.
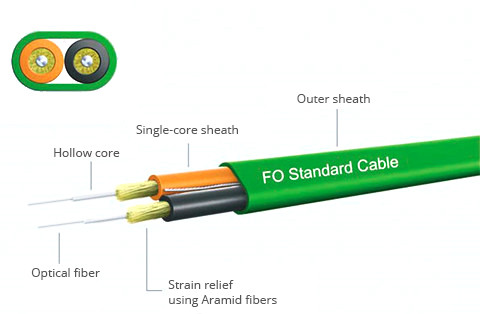
Plastic optical fibers differ from glass optical fibers in the following aspects.
- Physical Properties
Plastic optical fibers boast of simpler and less expensive components, as well as greater flexibility, and resiliency to bending, shock and vibration. In addition, they are lighter in weight. Plastic optical fibers can be handled without special tools or techniques. You need not be trained to handle or install it. You just cut it with scissors, plug it and it works. All these make plastic fibers a lower cost alternative to glass fiber or copper at medium distances and bit rates of 10 Gbps. In contrast, glass optical fibers need more difficult handling and more delicacy. While being mechanically protected well, glass optical fibers have higher information transmission capacity with lower loss. Moreover, glass optical fibers are optimized for small spaces and small targets. They can be used with both visible red and infrared light and are compatible with a long list of fiber heads.
- Applications
Plastic optical fibers are commonly used for low-speed, short-distance (up to 100 meters) applications in digital home appliances, home networks, industrial networks and car networks. Plastic fibers have an important position in military communication network and multimedia equipment in the data transmission. By comparison, glass fiber optic cables can be applied for longer-distance transmission at higher-speed in office networks. What’s more, they are adept to hostile conditions, more durable than their plastic counterparts.
As fiber technology continues to become more flexible and less expensive, plastic fibers are generally more cost effective than glass fiber optic cables and are ideal for applications that require continuous flexing of the fiber. No matter plastic optical fibers or glass optical fibers, before selection, you need to distinguish one from the other, and then choose the one that best suits your network demands. This post has described the difference between plastic fiber and glass fiber. Hope it can help you make clear these two kinds of fibers.
Related Article: MTP Link Performance: Higher Fiber Count vs. Lower Fiber Count