The present data center demand for transmission speed at the access layer can be handled with 10G over standard LC fiber optic cable. But with the increasing demand for high bandwidth in data centers as they expand, the network core and convergence layer will require the migration for 40/100G transmission. To meet this demand, MTP technology offers an ideal solution. MTP cable is designed for 40/100G transmission, and can accommodate 8/12/24/48 and even more fibers in one MTP connector that occupies less space and brings better conditions for airflow. This article will focus on MTP cable, introducing its basic information, and usage for 40G migration.
What Is MTP Cable?
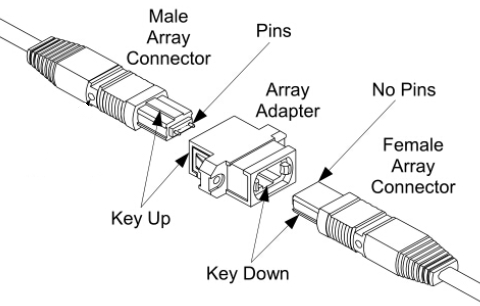
MTP stands for multi-fiber termination push-on connector, which is a registered trademark of US Conec. MTP Wiki defines it as a brand name for a version of MPO connectors with improved specifications. MTP and MPO connectors are completely compatible and inter-mateable: an MPO cable can be plugged into an MTP outlet and vice versa. But note that, MTP connector is designed with better mechanical and optical performance. MTP connectors use a special design, which is available in female (without pins) and male (with pins) versions as shown in the following picture. The pins can ensure proper alignment of the connectors when mating two MTP connectors. MTP connectors also have an extrusion, called a “key”. “Key up” and “key down” are the two types of the “key”. “Key up” means that the extrusion on the connector is facing up, while “key down” means facing down. MTP fiber optic cable can bring together 8/12/24/48 fibers in a single MTP interface, which increases the cable density, and offers savings in circuit card and rack space. Commonly, MTP cable is used for 40G/100G transmission.
Figure 1: MTP Connector Example
MTP Cable Types
To help customers achieve 40/100G connection and upgrade, FS has released several MTP cable types: MTP trunk cables, MTP harness cables and MTP conversion cables.
- MTP trunk cables are designed with MTP connectors (female/male) on both ends, and serve as permanent fiber links between panels in a structured environment. Typically, MTP cables are used as backbone or horizontal cable interconnections. Featured with efficient plug-and-play design, MTP trunk cable helps reduce the installation and maintenance costs. And MTP trunk cables can decrease the cable volume and improve the airflow conditions. FS offers 12/24-fiber MTP female trunk cables, which is design for 40/100G direct connections and high-density data center applications. They are available in various length (1-10m or customized length), and offer OM3/OM4 and OS2 with OFNP and LSZH cable jacket options. These cables are made of Corning ClearCurve® glass fibers with low insertion loss. All the MTP fiber cables have been fully tested to deliver super performance and reliability.

Figure 2: MTP Trunk Cable
- MTP harness cable is also called MTP fan-out or breakout cable. It’s terminated with a female/male MTP connector on one side and four or six duplex LC/SC connectors on the other side. Usually, this MTP cable type is used to connect devices within one rack for short distances links. FS provides 8-fiber MTP female to 4 LC harness cables, and 12-fiber MTP female to 6 LC harness cables. These breakout cables provide transmission from 8/12-fiber MTP to 4/6 LC duplex connectors, which is ideal for 10G to 40G and 25G to 100G transmissions.
Figure 3: MTP Breakout Cable
- MTP conversion cable is terminated with one MTP connector on one side and two or three MTP connectors on the other side. FS offers 24-fiber MTP female to 2x MTP female or 3x MTP female cables, or even the customized design. Usually, for the 1×2 MTP conversion cable, a single MTP connector holds 24 strands of fibers will be divided into 2 MTP connectors on the opposite end holding 12 fibers each. It allows users to convert the 12 fiber backbone trunks into Base-24 connections so that 40G or 100G data rates can be achieved. While 1×3 MTP conversion cable allows users to convert their 8-fiber backbone trunks into a single 24-fiber MTP connector for deploying 100G or 120G.
Figure 4: MTP Conversion Cable
Use FS MTP Cable for 40G Migration
Here introduces 2 common ways to upgrade 10G to 40G via MTP cable.
The first option is using a standard 12-fiber MTP trunk cable, 4 LC to LC patch cables, one 40G QSFP+ MTP transceiver, 4 SFP+ modules and a MTP-8 breakout cassette to achieve a simple migration from 4x10G to 40G. The figure below shows the connectivity method. Plug the 40G module into the QSFP+ port of a network switch, and plug the 4 10G modules into 4 SFP+ ports on another switch. Then use the MTP trunk connect the 40G module and the MTP cassette, and use the 4 LC cables connect the MTP cassette and the four 10G modules. Then the whole simple connection from 4x10G to 40G is completed.
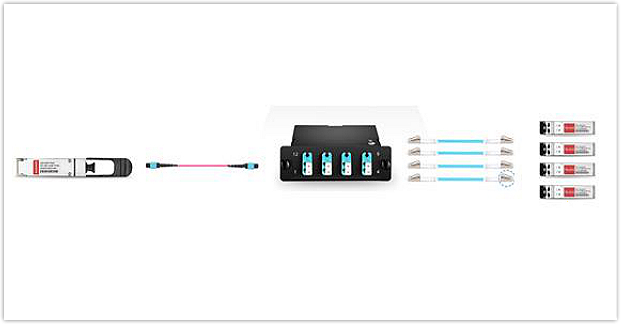
Figure 5: Use MTP trunk cable to achieve 40G migration.
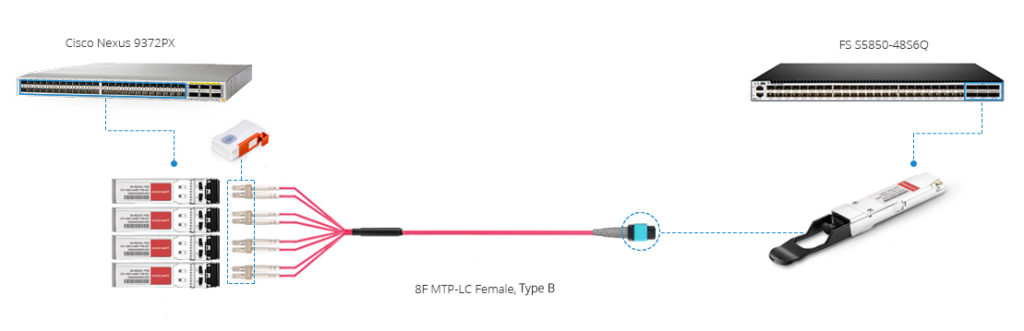
The other option is to use MTP breakout cable, which is a simple way. As the following picture shows, four 10G SFP+ transceivers are inserted into 4 SFP+ ports of the network switch, while one 40G QSFP+ module is plugged into QSFP+ port of the other switch. Then use the 8-fiber MTP to LC cable to connect the four 10G transceivers and the 40G transceiver. Finally, the data can be delivered from 10G to 40G switch via the MTP to LC breakout cable smoothly.
Figure 6: Use MTP to LC breakout cable to achieve 40G migration.
MTP cable is an important component for today’s high-speed transmission environment. It provides a flexible, high-density option for quickly connecting network devices. FS offers all the three MTP cable types as well as the patch cable to fit your most demanding and precise requirements. With 24/7 online technical and customer services, and most products are available in same-day shipping, FS will continue to offer better services for global customers.