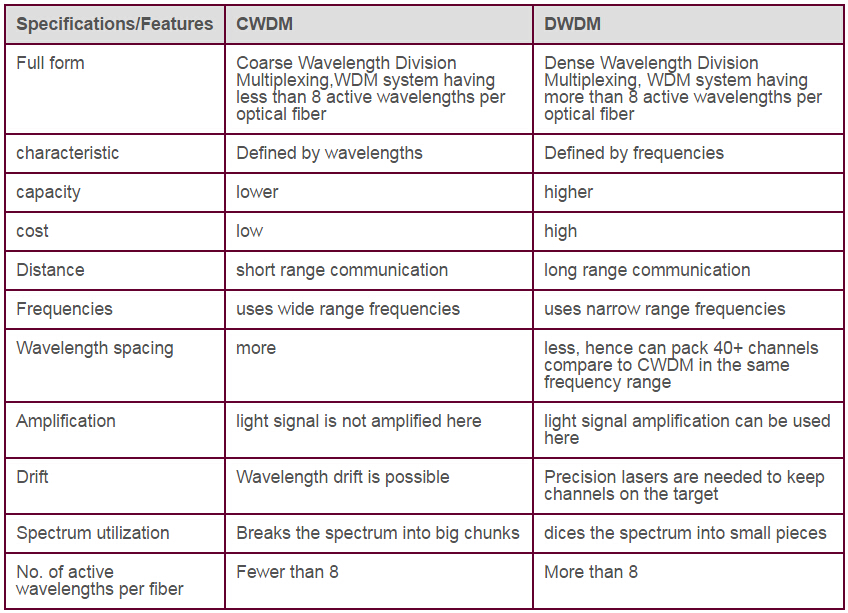
Transporting a single data stream through an optical fiber can be costly and inefficient. Wavelength Division Multiplexing (WDM) technology can transmit multiple, independent data streams through a single optical fiber to better utilize the bandwidth of the given optical fiber. Each data stream adopts a different wavelength of light (also know as lambda λ) and the data streams travel through a single fiber. With WDM, multiple cloud tenants can share the same optical fiber. Closely spaced wavelengths provide a higher number of channels (or bandwidth) per fiber. According to the wavelength spacing, WDM technology can be divided into two parts: Coarse WDM (CWDM) and Dense WDM (DWDM). This post aims to make a comparison between CWDM and DWDM.
Although both CWDM and DWDM use a multiplexer at the transmitter to join the signals together, and a demultiplexer at the receiver to split them apart, they still posses different features. This part will have a comparison between CWDM and DWDM from the following aspects.
Channel spacing is one of the differences between CWDM and DWDM. CWDM has wider channel spacing, typically 20 nm. DWDM has a much narrower wavelength spacing, typically 0.8 nm. With wider channel spacing, CWDM channel numbers available on the same link are significantly reduced. But the optical interface components in CWDM network do not have to be as precise as in DWDM network. So deploying CWDM network is much cheaper than deploying DWDM network. CWDM is defined by wavelengths, while DWDM is defined by frequencies.
DWDM deploys cooled distributed-feedback (DFB), while CWDM is based on uncooled distributed-feedback (DFB) lasers and wide-band optical filters. These technologies provide several advantages to CWDM systems such as lower power dissipation, smaller size, and less cost. The commercial availability of CWDM systems offering these benefits makes the technology a viable alternative to DWDM systems for many metro and access applications
CWDM distance is shorter than DWDM distance. CWDM is designed for short-distance fiber transmission, but DWDM is often implemented in a ultra long-haul optical transmission systems. The maximum DWDM link distance is dependent on the components used along the link, such as DWDM EDFA, DCMs, VOAs, OADMs, etc. CWDM cannot travel long distances because the CWDM wavelengths cannot be amplified with EDFA amplifiers, and therefore CWDM distance is limited to 100 miles (160 km).
Note: Additional DWDM latency will occur during the regeneration process in DWDM network.
For many SAN engineers, DWDM is the ideal SAN extension mechanism since it provides very high scalability, very low and predictable latency, and moderately long distance. The main benefit of CWDM is its low cost. It is a cheaper solution than DWDM. In other words, CWDM is optimized for cost, while DWDM is optimized for bandwidth. For enterprises that have access to dark fiber and have only limited scalability requirements, CWDM is a relatively inexpensive way to achieve low-latency and high-bandwidth interconnections between DCs. Moreover, the CWDM implementation also results in less complex installation, configuration, and operation as compared to DWDM.
However, viewing ultra long-haul fibers, where laying fibers can be major investment of the whole transmission system, the high cost of optical lasers can largely overwhelmed by the high cost of fiber deployment. Thus, transmitting a maximum number of wavelengths in each fiber can achieve the best total cost saving for the whole system. In addition, in a long-haul transmission system, DWDM is often integrated with all optical amplifier techniques such as EDFA and Raman Amplifiers, which amplifies signals in the optical domain without going through any OEO conversion processes as in the traditional systems.
In short, DWDM is a solution that provides a higher number of connections and longer reach, or extension, at a much higher cost while CWDM is a more cost-effective solution for metro or campus solutions where the distance is limited.
Other post you may be interested: CWDM & DWDM Mux/Demux Overview